1、#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
//值传递时,并不改变实参的值
void getmemory(char *p)
{
p=(char *) malloc(100);
strcpy(p, "hello world");
}
int main()
{
char *str=NULL;
getmemory(str);
printf("%s",str);
free(str);
return 0;
}
并且每次调用函数,都会泄露100大小内存空间

2、#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
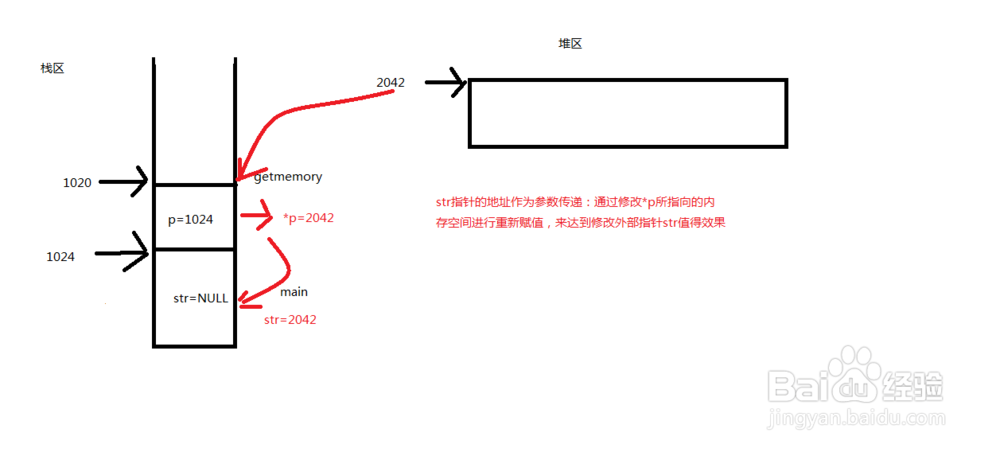
//实参地址作为参数传递,可以改变实参的值
void getmemory(char **p)
{
*p=(char *) malloc(100);
strcpy(*p,"hello world");
}
int main()
{
char *str=NULL;
getmemory(&str);
printf("%s\n",str);
free(str);
return 0;
}