1、plotyy(X1,Y1,X2,Y2)在左侧绘制X1与Y1之间的关系,左侧标记y轴;右在侧绘制X2与Y2之间的关系,右侧标记y轴。For example,plotyy(x1,y1,x2,y2,@loglog) % function handleplotyy(x1,y1,x2,y2,'loglog') % stringplotyy(X1,Y1,X2,Y2,'function1','function2')使用函数1(X1,Y1)绘制左轴数据和函数2(X2,Y2)绘制右轴数据
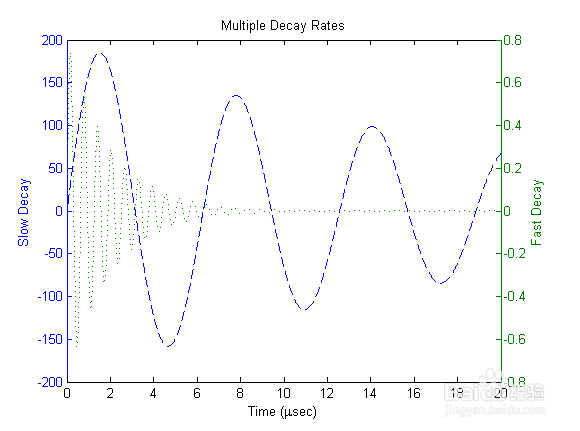
2、这个例子使用绘图作为绘图函数来绘制两个数学函数。 即使数据的相对值差别很大,两个y轴也可以在一个图表上显示两组数据。figurex = 0:0.01:20;y1 = 200*exp(-0.05*x).*sin(x);y2 = 0.8*exp(-0.5*x).*sin(10*x);[AX,H1,H2] = plotyy(x,y1,x,y2,'plot');set(get(AX(1),'Ylabel'),'String','Slow Decay')set(get(AX(2),'Ylabel'),'String','Fast Decay')xlabel('Time (\musec)')title('Multiple Decay Rates')set(H1,'LineStyle','--')set(H2,'LineStyle',':')
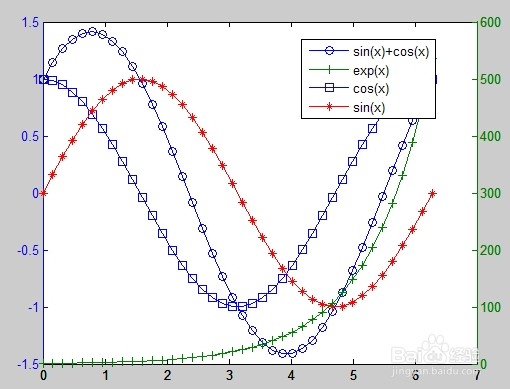
3、这个例子使用绘图作为绘图函数来绘制两个数学函数。 即使数据的相对值差别很大,两个y轴也可以在一个图表上显示两组数据。% 程序2:x=linspace(0,2*pi,40);[ax,h1,h2]=plotyy(x,sin(x)+cos(x),x,exp(x));set(h1,'linestyle','-')set(h2,'linestyle','-')set(h1,'marker','o')set(h2,'marker','+')hold onx=linspace(0,2*pi,40);hh=line(x,cos(x));set(hh,'linestyle','-')set(hh,'marker','s')hold onhhf=line(x,sin(x));set(hhf,'color','r')set(hhf,'linestyle','-')set(hhf,'marker','*')legend([h1,h2,hh,hhf],'sin(x)+cos(x)','exp(x)','cos(x)','sin(x)',0);